 In the last months, the theme of blockchain has raised in importance in the debate worldwide. Not only in terms of “Bitcoin Bubble” but also as the “next big unlock”.
In the last months, the theme of blockchain has raised in importance in the debate worldwide. Not only in terms of “Bitcoin Bubble” but also as the “next big unlock”.
Blockchain technology is a sort of backbone of a new type of internet. Don & Alex Tapscott, authors of the book “Blockchain Revolution” affirm: “The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.”
Based on transparency (data is embedded within the network, that is public by definition) and incorruptible (a huge amount of computing power is needed to override the entire network), blockchain could solve the problem of trust. According to Vitalik Buterin, the inventor of Ethereum, in the western countries, the majority of people trust public institutions, banks, organizations and corporations such as Facebook, Google and so on but in the rest of the world, there is a problem in this respect.
Initially, Bi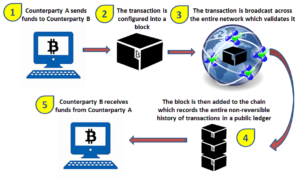 tcoin was the raison d’etre of the blockchain as it was originally conceived. By design, decentralization is a key aspect of this technology design, as well as the peer to peer relationship which is changing traditional transaction model, enabling the development of smart contracts (a digital protocol that automatically executes predefined processes of a transaction without requiring the involvement of a third party, as a bank). According to this, new bitcoins are provided by miners that compete to win bitcoins by solving computational puzzles in a decentralized way because the possibility to win bitcoins is a form of game theory to reward who decides to join the network[1]. Therefore, Bitcoin is managed by its network, not by a central authority as in the case of traditional currency.[2]
tcoin was the raison d’etre of the blockchain as it was originally conceived. By design, decentralization is a key aspect of this technology design, as well as the peer to peer relationship which is changing traditional transaction model, enabling the development of smart contracts (a digital protocol that automatically executes predefined processes of a transaction without requiring the involvement of a third party, as a bank). According to this, new bitcoins are provided by miners that compete to win bitcoins by solving computational puzzles in a decentralized way because the possibility to win bitcoins is a form of game theory to reward who decides to join the network[1]. Therefore, Bitcoin is managed by its network, not by a central authority as in the case of traditional currency.[2]
It is now recognized to be only the first of many potential applications of the technology.
Blockchain technology shows a lot of promise. Other than being used to execute energy supply transactions, it could also provide the basis for metering, billing and clearing processes. Other possible areas of application are in the documentation of ownership, the state of assets (asset management), guarantees of origin, emission allowances and renewable energy certificates. Blockchain technology has the potential to radically change energy as we know it, by starting with individual sectors first but ultimately transforming the entire energy market.
In Brooklyn, N.Y., taking advantage of small and secure transaction costs guaranteed by blockchain technology, companies are developing a way to use blockchain technology to enable solar panel owners to swap the output of their panels with their neighbors. That project brings together blockchain technology provided by Samsung for a microgrid developed by LO3, a start-up based in New York that develop microgrids using blockchain to enable local energy trading.
Despite skepticism about the viability of blockchain technology, it could be useful for company. A project to evaluate the use blockchain technology to help integrate renewables into the grid is developing in Germany: grid operator TenneT TSO[3] and German storage company Sonnen are working to make it real.
Sonnen is working on a community-based model for solar power and battery storage. Using a blockchain solution designed and developed by IBM (built with Hyperledger Fabric, a blockchain framework implementation and one of the Hyperledger projects hosted by The Linux Foundation), and residential storage batteries from Sonnen, the TenneT project intends to ascertain the extent to which these technologies help reduce the need for emergency measures.
Philipp Schröder, Managing Director and Chief Sales & Marketing Officer at Sonnen said in a statement that “The future of power generation will be composed of millions of small, decentralized power sources, including both prosumers and consumers. The blockchain technology is what makes mass simultaneous exchange between all these parties possible in the first place, and is thus the missing link to a decentralized, completely CO2-free energy future.”
We are living in an age in which a growing number of people have understood the need for retreat from nuclear and fossil-fuel energy. The importance of renewable energy is increasing steadily, so wasting less wind and solar power because of inability to transport it, it is a crucial element in the process of better integrating decentralized renewable energies and ensuring energy supply.
[1] Nowadays, research estimates that there are more than 700 cryptocurrencies already available
[2] Another problem solved by blockchain technology concerns privacy thanks to public and private keys.
[3] TenneT is a European electricity transmission system operator (TSO) with its main activities in the Netherlands and Germany.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————
Oltre che per le transazioni finanziarie incentrate su Bitcoin, la blockchain sembra potersi applicare anche in altri ambiti come quello energetico. In questo campo, uno dei progetti più avanzati prevede l’integrazione dell’energia rinnovabile prodotta in modo decentrato all’interno della rete elettrica.
